The Japanese yen has recently been depreciating against other currencies.
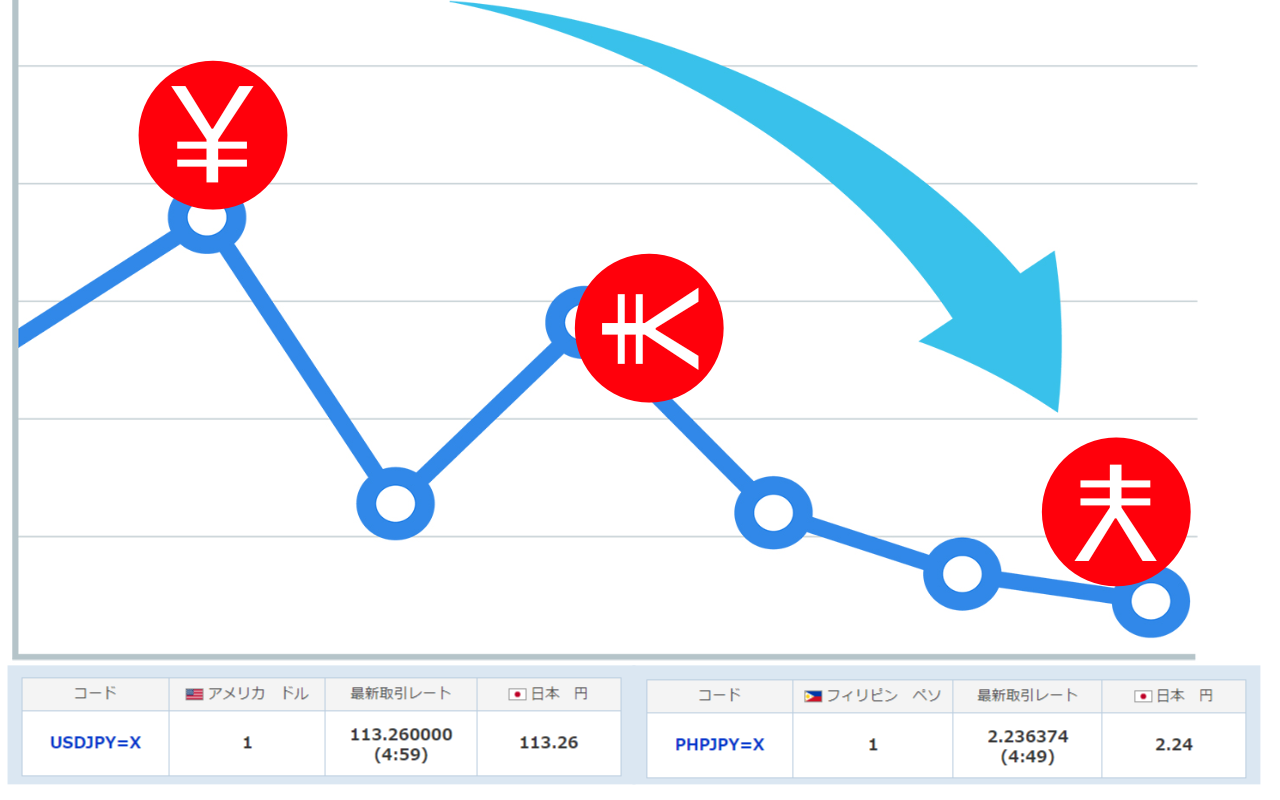
Ten years ago, the price of the dollar was as high as 77 yen per dollar, but after an abnormal drop to 125 yen per dollar due to Abenomics, the price settled at 110 yen per dollar.
However, in the last few days, the price has been dropping steadily to 113 yen.
It is difficult to determine what the appropriate exchange rate is because it depends on a variety of factors.
Even so, I think the yen is too weak at present.
There is a thing called the Big Mac Index. This is an estimate of purchasing power parity based on the price of a Big Mac in each country.
According to the 2021 edition, the price of a Big Mac in the United States is $5.65. In Japan, the price is $3.55 (390 yen).
Based on this index, the appropriate exchange rate is 69 yen to the dollar.
By the way, the price of a Big Mac in the Philippines is $2.82 (142 pesos), which is 316 yen in Japanese yen.
Most Japanese are not usually aware of the exchange rate, but if you are sending money to your family in the Philippines like I am, you have to be sensitive to it.
In addition, after moving to the Philippines, I will be receiving my pension in the local currency. If the yen goes down, the amount of money I receive will go down.
I have been accumulating dollars every month to avoid risk.
Although my assets have increased in yen terms, I am not happy at all. The stronger the yen, the better.
Tourists who come to Japan from abroad have a reputation that everything in Japan is cheap and the quality and service is excellent.
On the contrary, Japanese who travel abroad find the prices of goods in their destinations to be high.
For example, in Singapore, which is easily accessible from Japan, hotels and food are expensive. By the way, the price of a Big Mac is $4.31 (474 yen).
Even in Thailand, which I used to think was inexpensive, the price of a Big Mac is $3.9 (429 yen), which is more expensive than in Japan.
When Japan was earning foreign currency through overseas exports, it was said that a cheap yen was advantageous because it made prices more competitive, but the trade balance for 2019 is only a 1 trillion yen surplus. In recent years, the trade balance has sometimes been in the red.
On the other hand, the balance of dividends and interest from overseas investments is a surplus of 21 trillion yen. In other words, Japan is now a country with a very large return on foreign investment.
If this return is converted from foreign currency to yen, the weak yen is not bad for investors.
This is the same way that overseas tourists enjoy a weak yen.
However, imports from overseas will become more expensive, so a weaker yen is not welcome by the people.
According to the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries, the food self-sufficiency rate last year was only 67% on a production value basis. In other words, 33% of our food is imported from overseas, which means that when the yen weakens, the price of food goes up.
Of course, in the case of agricultural products, the price is affected by the production output of the production area, so the exchange rate alone does not necessarily determine the price, but it is a fact that food prices have been slowly rising in recent years.
Even though the exchange rate is not the only indicator of a country's economic strength, further depreciation of the yen is not welcome.